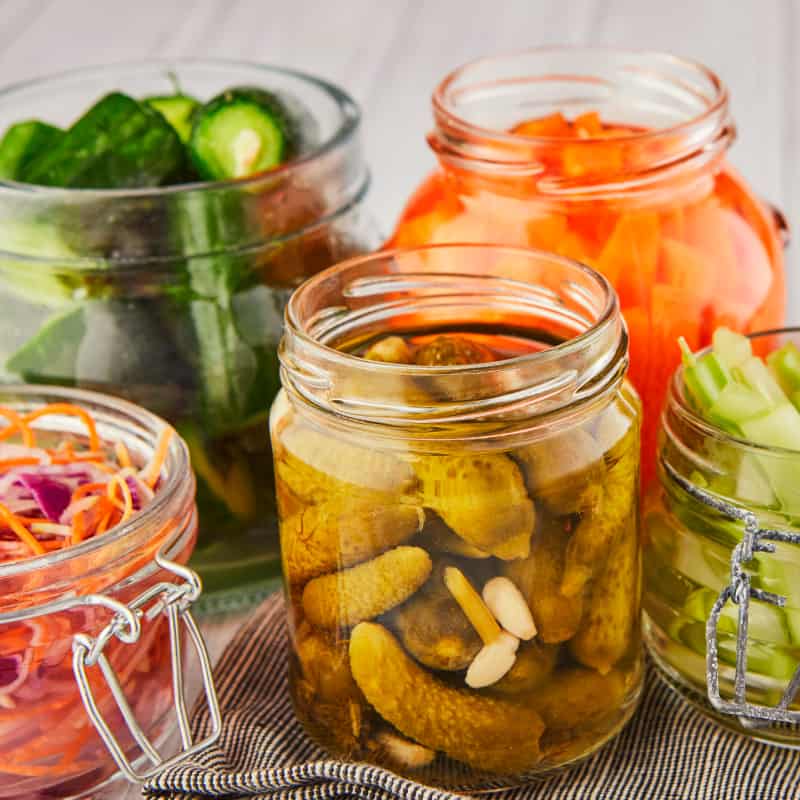
Are you looking for a way to improve your health and fitness? If so, you may consider adding fermented greens to your diet. Fermented green vegetables and greens are packed with nutrients that can help boost your energy and support your immune system. Here are the top ten reasons to add fermented greens to your diet.
Fermented Foods and Probiotics
Fermented foods are a great source of probiotics, which are live bacteria with many health benefits. Probiotics are important for gut health and can help improve the immune system and reduce inflammation. Fermented foods are easy to make at home and offer a delicious way to get the probiotics your body needs.
10 Benefits of FermentedGreens and Vegetables, According To Science
Does the mention of fermented foods make your nose wrinkle up in disgust? It might be time to reconsider because fermented vegetables have amazing health benefits. Science has shown that they offer many advantages – here are eight.
#1 Way to Lower Your Cholesterol Naturally
Fermented greens are one of the best ways to lower your cholesterol naturally. When cholesterol is oxidized, it becomes dangerous to your health.
Fermented greens are packed with antioxidants that help to prevent this oxidation. In addition, fermented greens help to promote healthy bacteria in your gut. This healthy bacteria helps to break down cholesterol, making it less likely to be absorbed into your bloodstream.
As a result, regular consumption of fermented greens can help to lower your cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease significantly.
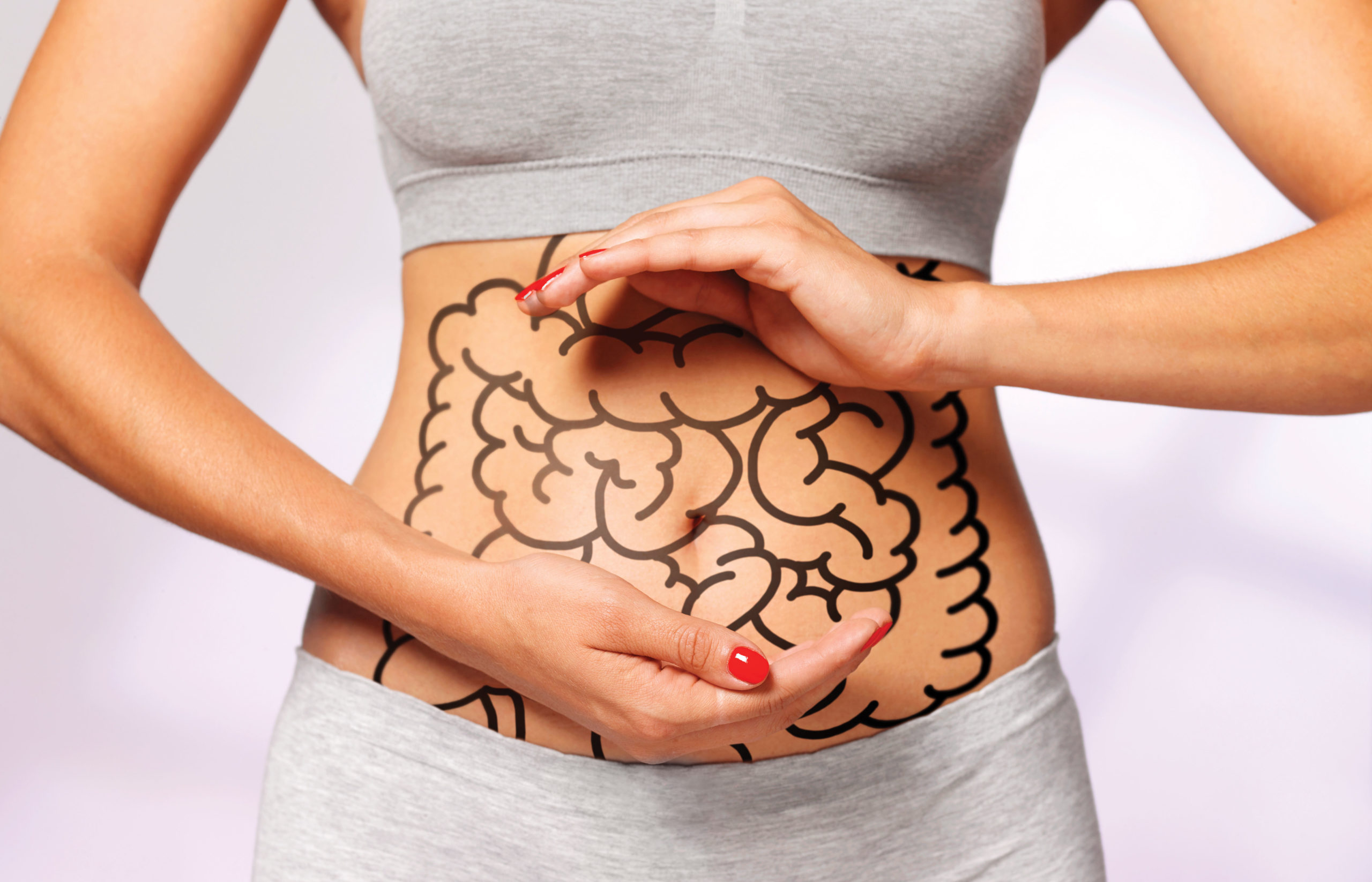
Fermented Vegetables Are Easier to Digest
For many of us, the word "fermented" conjures up images of sour pickles or tangy sauerkraut. But what exactly is fermentation, and why would you want to eat fermented foods?
Fermentation is a process that occurs when beneficial bacteria break down carbohydrates in food. This process gives fermented foods their characteristic Tangy flavour and produces beneficial compounds like lactic acid and enzymes.
These compounds can help improve digestion, boost immunity, fight with iron deficiency and promote healthy skin. Fermented greens are an excellent source of probiotics, making them an ideal choice for people with sensitive stomachs or irritable bowel syndrome.
Fermented Vegetables Will Give You More Energy
Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, beneficial bacteria that help promote a healthy gut. A healthy gut is essential for good digestion and absorption of nutrients, both of which are necessary for energy production.
Additionally, fermented foods can help improve mood and reduce stress, increasing energy levels.
Fermented Foods are More Nutritious
Most people are familiar with fermentation in beer or winemaking, but fermentation can also be used to preserve food. Many of the world's most popular foods, such as cheese, bread, and yogurt, are fermented.
Fermentation is a process in which bacteria break down carbohydrates into lactic acid. This not only preserves food but also makes it more nutritious. The lactic acid produced during fermentation helps break down plants' cell walls, making it easier for the body to absorb the nutrients.
Additionally, fermentation promotes the growth of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that help to improve digestion.
Fermentation Helps Fight Inflammation
Fermentation is when microorganisms break down carbohydrates into alcohol or acids. This process can occur naturally in foods like yogurt, pickles, and bread. Fermented foods have been shown to offer several health benefits, including reducing inflammation.
Inflammation is a natural response to injury or disease, but chronic inflammation can lead to several health problems. Studies have shown that certain compounds in fermented foods can help to reduce inflammation.
Fermentation Strengthens Microbiota
The human gastrointestinal tract contains a complex and diverse community of microorganisms, which play an important role in maintaining gut health. Studies have shown that the composition of this microbiota can be affected by diet, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions.
Fermentation is one process that can have a positive impact on gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. This is because fermentation creates an environment rich in nutrients and oxygen, which is ideal for bacterial growth.
In addition, fermentation also breaks down difficult-to-digest carbohydrates, making them more available for gut bacteria to use as food.
Fermentation is a Safe Way to Preserve Foods
Fermentation is a great option if you're looking for a safe and effective way to preserve food. This ancient process involves using bacteria and yeasts to convert carbohydrates into alcohol or lactic acid. This prevents the growth of harmful microorganisms and preserves the food's nutrients and vitamins.
Additionally, fermenting foods can add beneficial probiotics to your diet. These "good" bacteria help to support a healthy gut, boosting immunity and overall health. While fermentation may seem like a complicated process, it's quite simple.
With a little time and effort, you can easily transform fresh fruits and vegetables into delicious fermented foods.
Fermentation Creates New Flavors
Fermentation is a process that has been used for centuries to preserve food and create new flavours. During fermentation, bacteria and yeast break down the sugars in food, which produces alcohol and carbon dioxide. This process can transform the flavour of a dish, making it more complex and nuanced.
Fermentation can also help to tenderize the meat and preserve vegetables. In recent years, fermentation has experienced a renaissance, with chefs and home cooks exploring its potential. From kimchi to kombucha, there are endless possibilities for incorporating fermented foods into your diet. So don't be afraid to experiment – you may just find your new favourite flavour.
Fermentation is Easy to Do
The process of fermentation has been used for centuries to preserve food. While it may seem complicated, fermentation is quite easy at home. You only need a clean jar, fresh fruit or vegetables, and a little time.
Let Us Show You How
- The first step is to wash your produce thoroughly and chop it into smaller pieces.
- Next, add the fruit or vegetables to the jar, along with a little bit of water.
- Once the jar is full, seal it tightly and store it in a cool, dark place.
Over the next few days, you will notice that the contents of the jar begin to bubble and ferment. This is a normal part of the process! Once the fermentation is complete, you can store the jar in your refrigerator for up to six months.
Fermentation Aids in the Slowing of the Aging Process
As we age, our bodies go through many changes. We may lose muscle mass, our skin may become thinner and less elastic, and our bones may become more fragile. These changes are all a natural part of the aging process.
However, there is some evidence to suggest that fermentation can help to slow down the aging process and even prevent the risk of stomach cancer.
Probiotics have been shown to improve immune function, digestion, and cognitive health. In addition, fermented foods contain high levels of antioxidants, which can help to protect cells from damage.
Best Fermented Foods From Around the World
If you're a fan of fermented foods, you're in luck – they're popular worldwide! Here are some of the best examples from different parts of the globe.
Ayran- Middle East
This refreshing drink is made by blending yogurt, water, and salt. It's popular in countries like Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Iran.
Doenjang- Korea
This fermented soybean paste is a staple of Korean cuisine. It adds flavour to soups, stews, and other dishes.
Curd – India, Pakistan
Curd is a common fermented food made from milk and yogurt in India. It's eaten for breakfast or as a snack, and it's considered to be healthy probiotic food.
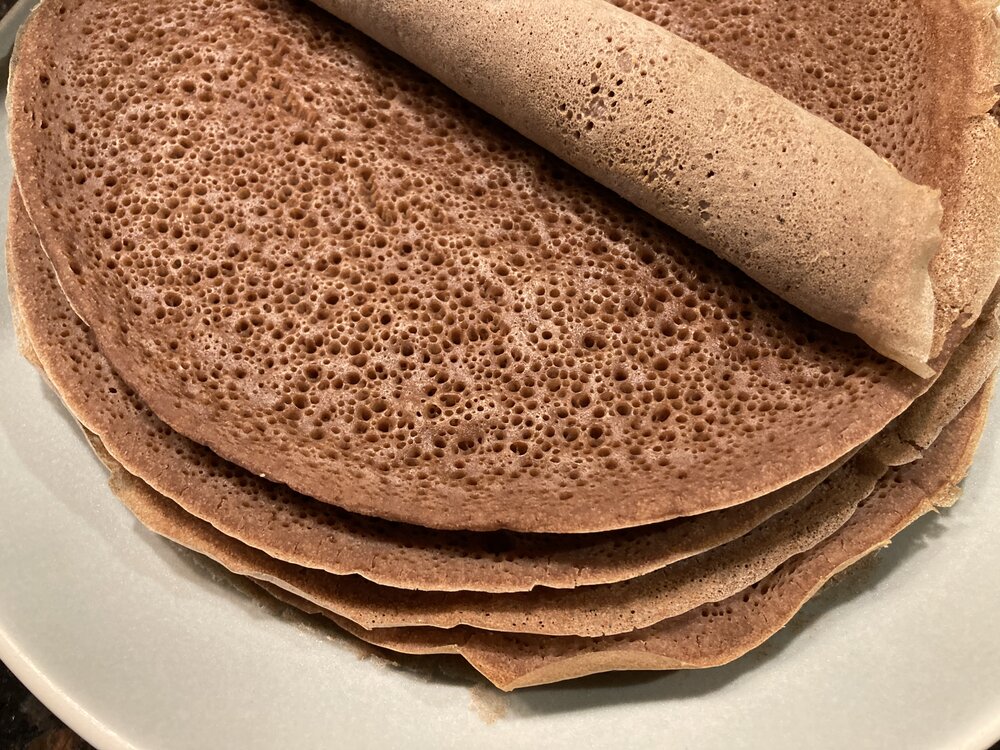
Injera – Ethiopia
This spongy, fermented bread is a staple of Ethiopian cuisine. It's made from a grain called teff, often used to scoop up stews and other dishes.
Kefir- Europe
Kefir is a fermented milk drink popular in many parts of the world. It's made by adding kefir grains to milk and has a slightly sour taste.
Kimchi – Korea
In Asia, kimchi is a popular fermented dish made with cabbage and chilli peppers. It's often served as a side dish or condiment.
Kombucha – China, Europe
Kombucha is a fermented tea made from black tea, sugar, and bacteria or yeast. The fermentation process produces a variety of acids and probiotics that give kombucha its distinctive sour taste.
Sourdough Bread - Europe, North America
Sourdough bread is a type of bread that is made from fermented dough. The starter culture is made from yeast and lactobacilli, two types of bacteria.
Sourdough bread has a sour, tangy taste that is different from other types of bread.
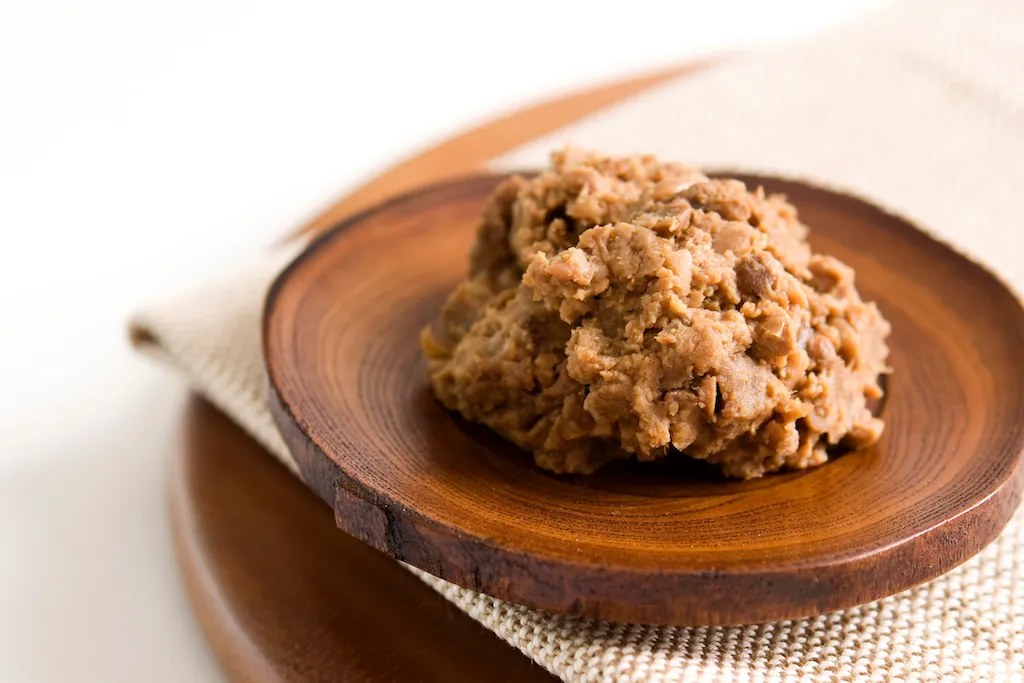
Miso – Japan, Korea
Miso is a Japanese fermented food that is made from soybeans and rice. It has a salty and savoury taste and is often used to add flavour to soup, stew, and other dishes. Miso is a healthy food source of probiotics, protein, vitamins, and minerals. It is also believed to have anti-inflammatory properties.
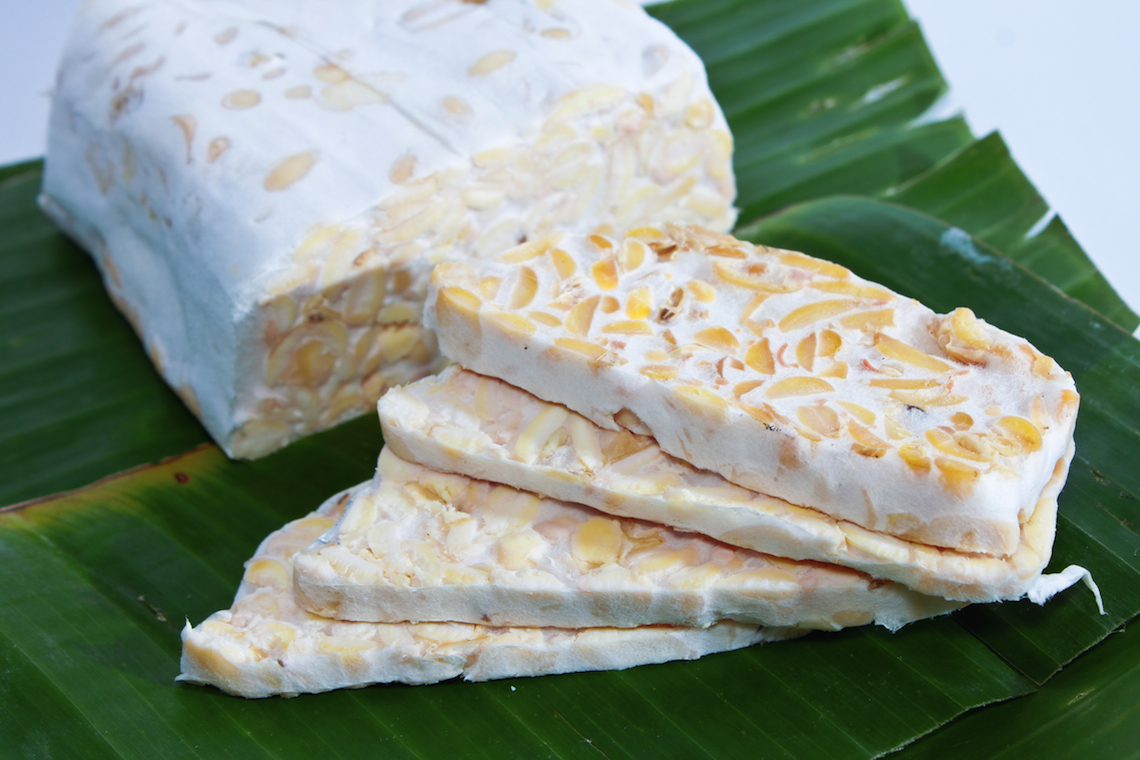
Tempeh – Indonesia
Tempeh is a fermented soybean cake that is popular in Indonesia. It is made from whole-cooked soybeans and mashed into a thick paste. The paste is then mixed with a grain such as rice, millet, or barley, and the mixture is incubated until it forms a solid cake. Tempeh has a nutty taste and a firm texture.
Pulque – Mexico
In Mexico, a dish called pulque is made from fermented agave sap.
Pickles - Eastern Europe
Pickles are cucumbers soaked in brine (water, vinegar, and salt) mixed with spices. The cucumbers ferment in the mixture, developing a sour, tangy flavour over time.
Sauerkraut – Across Europe
And in Europe, sauerkraut is a classic fermented food made from white cabbage. It's usually served with sausage or pork, and it's a great source of probiotics.
Smetana (Sour cream) - Ukraine
Sour cream is a dairy product that's made from fermented cream. It has a thick, creamy texture and a slightly sour taste. It's popular in countries like the United States, Canada, and Ukraine, and it's used as a condiment or dip.
Hákarl – Iceland
Hákarl is a traditional Icelandic dish that's made from fermented shark meat. It's usually eaten as a delicacy and has a strong, fishy flavour.
Kvass-Eastern Europe
Kvass is a fermented beverage popular in Russia and other Eastern Europe. It's made from rye bread, water, and yeast and tastes sour and slightly salty. Kvass is low in calories and carbohydrates and is a good source of B vitamins and probiotics. It's also been traditionally used as a remedy for gastrointestinal problems.
There are many other delicious examples of fermented foods from around the world – so why not explore them all? Who knows? You might just find your new favorite dish!
This is What Happens in Your Gut When You Eat Fermented Foods
When you eat fermented foods, like yogurt or sauerkraut, the live and active cultures in the food help to keep your gut healthy, these cultures are beneficial bacteria that help to break down food, absorb nutrients, and keep harmful bacteria in check. In addition, fermented foods contain prebiotics, a type of dietary fibre that helps feed the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
The fermentation process also creates new nutrients, like vitamins B and K, not found in unfermented foods. As a result, eating fermented foods regularly can help to improve digestion and boost your immune system. Plus, it's a delicious way to add variety to your diet.
So next time you're looking for a nutritious snack, reach for some yogurt or kimchi - your gut will thank you!